Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT)
Highly sensitive, highly specific molecular testing performed in our CLIA-certified high-complexity laboratory.
Sensitivity commonly >90–95%, specificity >98%
Significantly reduces false negatives and false positives compared to serology
NAAT delivers the highest level of diagnostic confidence available today.
Timing changes outcomes
Identify infection earlier than antibody or antigen tests and enable faster diagnosis.
NAAT detects infection sooner — when clinical intervention matters most.
Multiplex testing detects multiple pathogens from a single specimen reducing repeat testing.
NAAT combines accuracy and efficiency without compromising care.
Our NAAT Workflow: Built for Accuracy at Every Step
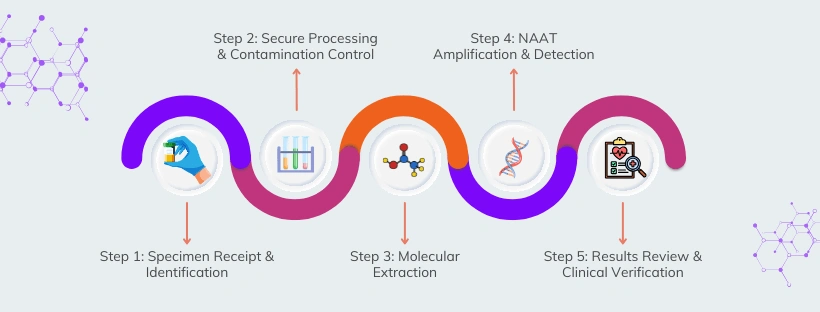
Specimen Receipt & Identification
What happens:
Specimen is received and logged into the laboratory information system
Unique identifiers are assigned to ensure full traceability
Why it matters:
Maintains chain-of-custody and prevents specimen mix-ups.
Secure Processing & Contamination Control
What happens:
Specimens are cataloged and staged for testing
Processing occurs in controlled biosafety environments
Strict separation of pre- and post-amplification areas
Why it matters:
Minimizes contamination and preserves result integrity.
Molecular Extraction
What happens:
Specimens are processed in biosafety cabinets
Target nucleic acids (DNA/RNA) are extracted using automated extraction systems
Reagents and controls are applied according to validated protocols
Why it matters:
Ensures consistent, high-quality molecular material for testing.
NAAT Amplification & Detection
What happens:
Extracted nucleic acids are amplified using validated NAAT platforms
Thermal cycling precisely heats and cools samples to detect target sequences
Internal controls verify test performance
Why it matters:
This is where NAAT’s sensitivity and specificity are realized.
Results Review & Clinical Verification
What happens:
Results are uploaded into the reporting system
All findings undergo dual verification
Final results are reviewed and signed by a physician
Why it matters:
Ensures accuracy, accountability, and clinical reliability.
The Gold Standard for Infectious Disease & Molecular Diagnostics
What is NAAT?
NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing) is a molecular diagnostic method that detects pathogen-specific DNA or RNA directly from patient samples. Unlike antibody or antigen testing, NAAT identifies active infection, not immune response. This testing method detects genetic material (DNA/RNA), identifies infection earlier, and is applicable across viral, bacterial, and fungal pathogens.
NAAT vs Traditional Testing
NAAT (nucleic acid amplification testing) is considered the clinical gold standard for many infectious disease diagnostics because it detects active infection directly and identifies pathogens earlier than other testing methods. NAAT offers high sensitivity (often greater than 90%) and high specificity, resulting in fewer false positives and more reliable results. In comparison, antibody tests do not detect active infection and rely on a delayed immune response, with more variable accuracy. Antigen tests may detect active infection in some cases but typically have moderate sensitivity and specificity, making them better suited as adjunct tests rather than primary diagnostic tools.
Accuracy & Performance of NAAT
Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) offers high analytical performance for the detection of active infection. Depending on the pathogen and specimen type, NAAT assays commonly demonstrate sensitivity greater than 90–95% and specificity exceeding 98%, supporting reliable identification of clinically relevant infections. By detecting pathogen-specific DNA or RNA, NAAT enables earlier detection than serologic testing, which relies on host immune response. Test performance may vary based on pathogen, specimen type, and clinical context.
False Positives & Negatives NAAT
False positive results with NAAT are uncommon and are most often associated with laboratory contamination or improper sample handling. At Genome-Based Diagnostics, these risks are minimized through strict laboratory protocols, internal quality controls, and high-complexity testing standards. False negative results may occur if testing is performed very early in infection or if specimen quality is insufficient. These risks are reduced through optimized collection methods and validated amplification protocols, supporting accurate and dependable results.
Clinical Benefits of Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing
NAAT provides meaningful clinical advantages by enabling earlier detection, reducing missed diagnoses through high sensitivity, and limiting unnecessary follow-up testing through high specificity. Multiplex testing capabilities allow simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens from a single specimen, improving efficiency and turnaround time. Together, these benefits support greater diagnostic confidence and informed patient management.
Limitations & Considerations
While NAAT is a powerful diagnostic tool, results should be interpreted within the appropriate clinical context. NAAT detects genetic material rather than infectivity, and residual nucleic acids may persist following successful treatment. As with all diagnostic testing, clinical correlation and provider judgment remain essential for optimal patient care.
GbDx NAAT Methodology
Genome-Based Diagnostics utilizes validated NAAT amplification protocols designed for accuracy, efficiency, and reproducibility. Our testing platform supports multiplex detection, rigorous quality control measures, and optimized specimen processing workflows. All testing is performed by an experienced molecular diagnostics team, following a standardized process from sample receipt through amplification, analysis, and clinical reporting.
Compliance, Certification, and Quality
All NAAT testing at Genome-Based Diagnostics is performed in a CLIA-certified high-complexity laboratory and adheres to stringent regulatory and quality requirements. We maintain HIPAA-compliant data handling, validated assays, and ongoing quality assurance programs to ensure consistent, reliable, and clinically actionable results for healthcare providers.
The Gold Standard for Infectious Disease & Molecular Diagnostics
What is NAAT?
NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing) is a molecular diagnostic method that detects pathogen-specific DNA or RNA directly from patient samples. Unlike antibody or antigen testing, NAAT identifies active infection, not immune response. This testing method detects genetic material (DNA/RNA), identifies infection earlier, and is applicable across viral, bacterial, and fungal pathogens.
NAAT vs Traditional Testing
|
Feature |
NAAT |
Antibody Test |
Antigen Test |
|
Detects Active Infection |
Yes |
No |
Sometimes |
|
Time to Detection |
Early |
Delayed |
Moderate |
|
Sensitivity |
High (>90%) |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Specificity |
High |
Variable |
Variable |
|
False Positives |
Low |
Higher |
Moderate |
|
Clinical Standard |
Gold Standard |
Legacy |
Adjunct |
Accuracy & Performance of NAAT
Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) offers high analytical performance for the detection of active infection. Depending on the pathogen and specimen type, NAAT assays commonly demonstrate sensitivity greater than 90–95% and specificity exceeding 98%, supporting reliable identification of clinically relevant infections. By detecting pathogen-specific DNA or RNA, NAAT enables earlier detection than serologic testing, which relies on host immune response. Test performance may vary based on pathogen, specimen type, and clinical context.
False Positives & Negatives NAAT
False positive results with NAAT are uncommon and are most often associated with laboratory contamination or improper sample handling. At Genome-Based Diagnostics, these risks are minimized through strict laboratory protocols, internal quality controls, and high-complexity testing standards. False negative results may occur if testing is performed very early in infection or if specimen quality is insufficient. These risks are reduced through optimized collection methods and validated amplification protocols, supporting accurate and dependable results.
Clinical Benefits of Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing
NAAT provides meaningful clinical advantages by enabling earlier detection, reducing missed diagnoses through high sensitivity, and limiting unnecessary follow-up testing through high specificity. Multiplex testing capabilities allow simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens from a single specimen, improving efficiency and turnaround time. Together, these benefits support greater diagnostic confidence and informed patient management.
Limitations & Considerations
While NAAT is a powerful diagnostic tool, results should be interpreted within the appropriate clinical context. NAAT detects genetic material rather than infectivity, and residual nucleic acids may persist following successful treatment. As with all diagnostic testing, clinical correlation and provider judgment remain essential for optimal patient care.
GbDx NAAT Methodology
Genome-Based Diagnostics utilizes validated NAAT amplification protocols designed for accuracy, efficiency, and reproducibility. Our testing platform supports multiplex detection, rigorous quality control measures, and optimized specimen processing workflows. All testing is performed by an experienced molecular diagnostics team, following a standardized process from sample receipt through amplification, analysis, and clinical reporting.
Compliance, Certification, and Quality
All NAAT testing at Genome-Based Diagnostics is performed in a CLIA-certified high-complexity laboratory and adheres to stringent regulatory and quality requirements. We maintain HIPAA-compliant data handling, validated assays, and ongoing quality assurance programs to ensure consistent, reliable, and clinically actionable results for healthcare providers.
